Reactants: Reactants are the starting substances in the chemical reaction.
Products: Products are the substances produced in a chemical reaction.
Conservation of Mass: Chemical equations show that atoms are conserved in the reaction; this is known as the conservation of mass.
Total mass of products = Total mass of reactants
Content Scribble
Acids
Properties of Acids: Acids have certain properties which distinguish it from bases:
- Taste sour
- Corrosive
- React with solid substances
Bases
Properties of Bases: Bases have certain properties which distinguish it from acids:
- Taste Bitter
- React with the hydrogen in acids
Indicators
Indicators are substances that can be used to tell whether a substance is an acid or base.
Types of Indicators
- An example of an indicator is litmus paper
- Acid turns blue litmus paper red
- Acids do not change the colour of red litmus paper
- Another example of an indicator used for acids is the metal test
- Acids wear away metals
- Hydrogen gas is given off while the metal is changing.
Universal Indicator & pH:
- pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution
- The lower the pH the more acidic the solution
- Strong acidic solutions have pH around 0 to 2
- The higher the pH the more basic the solution
- Strongly basic solutions have pH around 12 to 14
Chemical Reactions:
- A chemical reaction is when substances combine to form new substances.
- Indicated by change in colour or odour
- Exothermic (gives off heat)
- Endothermic (heat is absorbed)
- Gas is given off
A chemical equation: chemical equation summarises the events of a chemical reaction.
Types of chemical reactions:
- Metal/acid Reaction: acid + metal = salt + hydrogen gas
- To test for the presence of hydrogen gas, you bring a lit taper next to the gas and it should pop. The name of the salt changed depending on the name of the acid and metal.
- I.E: Hydrochloric Acid + Magnesium = Magnesium Chloride + Hydrogen
- Neutralisation: acid + base = salt + water
- I.E: Sulfuric acid + calcium Hydroxide = calcium + water
- Acid/carbonate Reaction: acid + carbonate = salt + carbon dioxide + water
- In another words, acid carbonate reaction is when limewater goes from visible to cloudy/turbid.
- Nitric Acid + calcium carbonate = calcium nitrate + Co2 + H2o
- Combustion: The reaction typically gives off heat and light. The general equation for a complete combustion reaction is
- Fuel + O2 → CO2 + H2O.
- Corrosion: is the eating away of metal so that it loses strength and become unable to do its intended purpose.
- Precipitation: the formation of a solid from 2 solutions.
- Neutralisation: the reaction between an acid and a base
- Decomposition: the breaking of a compound into more simple substances.
Period Table
The Arrangement of the Periodic Table
- The elements are arranged in the periodic table according to their increasing atomic number
- The elements are arranged in rows and columns
- Rows are called periods
- Columns are called groups
Recognising the Elements on the Periodic Table
- Each element is represented in a separate box on the period table
- Each box has four different characters:
- the atomic number
- the symbol of the element
- the atomic weight
- the name of the element
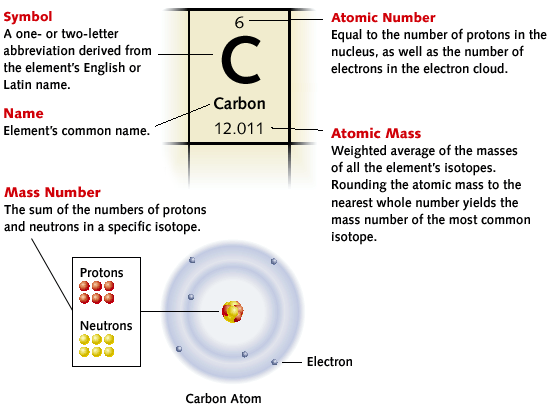
Atoms
Structure of an atom:
the atoms of all matter are electrical and are made up of three small subatomic particles:
- Electrons: which carry negative charges
- Protons: which carry positive charges
- Neutrons: which carry no charge
Protons and neutrons make up the very dense nucleus of the atom and the tiny electrons are arranged in shells of different energy levels and orbit around the nucleus.
The maximum number of electrons in the first shell is always two, the second is eight and the third is eight. Electrons fill the inside shells first.
Attractions
- Atoms are held together by a strong attraction between protons and electrons.
- Particles with opposite charges attract one another.
- E.g. opposite poles of a magnet.
- The attractions of the ions form new compounds.
- More electrons than electrons is negative.
- More protons than electrons is positive.
- The electrons and protons keep the compound together.
- The chemical bond is called ionic bond.
- The difference in charge keeps them together.
- A compound stays together because they share electrons and protons from each other.
Definitions
- Atom: an atom is the smallest unit in an element that can exist by itself.
- Molecule: a molecule is 2 or more atoms joined together.
- Element: element is made from one type of atoms only.
- Compound: a compound is made up from many molecules joined together.


0 Comments